Tiered Storage: Best Practices for Optimal Data Management
With the average cost of storing a single TB of file data at $3,351 per year, your business needs a solution that cuts these expenses and streamlines access to your essential files.
One way to achieve that is by utilizing storage tiering - a pivotal strategy for reducing storage fees and ensuring critical data is always at your fingertips. Learn about tiered data storage to optimize data management and boost your organization’s efficiency.
What You’ll Learn:
- Find out how to ensure your critical data is stored on high-performance media for quick and reliable access.
- Understand how tiered storage supports data security and compliance, protecting sensitive information.
- Discover strategies to quickly restore data and minimize downtime in case of an outage or data loss.
What Is Tired Storage?
Tiered storage is a smart data management method that organizes data based on its importance and frequency of access. High-priority data goes on fast, expensive storage like SSDs, while less critical data is stored on cheaper, slower media like HDDs or cloud storage.
This way, businesses get the best performance for crucial tasks and save money on less essential storage needs – it’s like keeping everyday items handy and storing seldom-used things in the attic.
What Is Storage Tiering?
Storage tiering involves organizing your data into multiple layers based on its use and priority. It's also called tiered storage, so be aware of this when reading various sources, as they might use different naming conventions.
Nevertheless, both terms refer to the same concept, which involves:
- keeping storage costs under control
- ensuring optimal performance for critical tasks
- helping businesses efficiently balance speed, accessibility, and expense
Storage Tiering: Data Classes
With 85% of production data being inactive and only 10-20% actively used, tiered storage helps simplify data management processes. It ensures that your vital data is quickly accessible while less frequently used data is stored cost-effectively.
Here's a breakdown of the four primary data classes:
- Mission-Critical Data: The most critical data requires the highest performance and availability. It's stored on the fastest and most reliable storage media, such as SSDs or NVMe drives, to ensure zero downtime and quick access.
- Hot Data: Frequently accessed data that supports day-to-day operations falls into this category. It demands high performance but can tolerate slightly slower speeds than mission-critical data. SSDs or high-performance HDDs are typically used for hot data.
- Warm data is accessed regularly but less often than hot data. It includes older transaction records, monthly reports, and other types of data that require availability but not instantly. Warm data is usually stored on cost-effective HDDs or hybrid storage solutions.
- Cold Data: Rarely accessed data that must be retained for regulatory or archival purposes is considered cold data. You can keep it on the most economical storage options, such as cloud or tape storage, where cost-efficiency is prioritized over access speed.
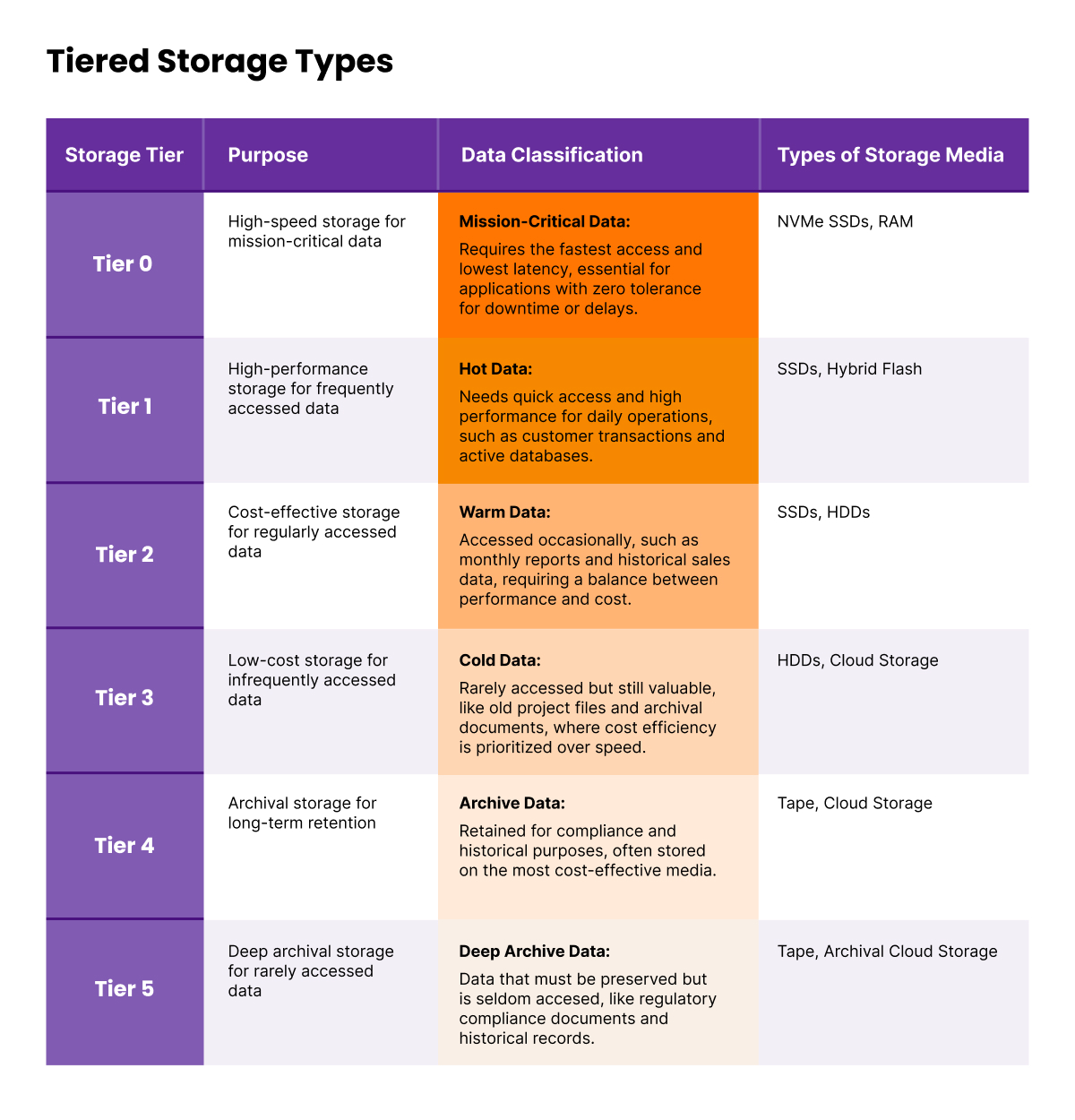
Tiered Storage Types
Since installed storage capacity is forecast to grow at an annual growth rate of 19.2%, reaching 180 zettabytes by 2025, understanding tiered storage types is fundamental.
The 5 Benefits of Storage Tiering
Research shows that using a four-tiered storage system can lead to up to 98% cost savings compared to untired storage. Besides this significant cost reduction, find all the benefits of tiered storage below.
Cost Reduction
Implementing storage tiering can lead to significant cost savings by ensuring that only the most critical data is stored on high-performance, expensive media, while less critical data is placed on more economical storage options.
Improved Data Management
Storage tiering helps streamline data management processes, making it easier for IT managers and backup administrators to categorize and store data based on its importance and usage frequency.
Enhanced Performance
By ensuring that high-priority data is stored on fast, high-performance media, storage tiering improves overall system efficiency and enhances user experience by providing quick access to essential data.
Increased Data Security and Compliance
Storage tiering supports secure and compliant storage solutions, helping organizations protect data and meet regulatory requirements. It assures that data is kept in a manner that adheres to industry standards and legal mandates.
Robust Disaster Recovery
Effective data backup and recovery strategies are crucial for minimizing downtime in case of an outage or data loss. Storage tiering supports these strategies by categorizing data and quickly restoring it when needed.
Tiered Storage vs. Data Caching: Key Differences
While both storage tiering and data catching aim to optimize data access and storage efficiency, they operate in distinct ways.
Storage tiering categorizes data into different layers based on usage and importance, using various storage media, such as SSDs for critical data and HDDs for less frequently accessed data.
Data caching temporarily stores copies of frequently accessed data in high-speed storage like RAM or SSDs for quick access. When data is requested, the system checks the cache first, speeding up retrieval if the data is present.
Key Differences:
- Purpose: Tiering focuses on long-term data placement for cost and performance optimization, while caching aims to speed up short-term data access.
- Operation: Tiering moves data between storage media based on policies, while caching creates temporary copies of frequently accessed data.
- Usage: Tiering is ideal for managing large data volumes with varying access needs, while caching enhances speed for applications requiring rapid, repetitive data access.
Integrating Ootbi into Your Storage Tiering Strategy
Ransomware-proof and immutable out-of-the-box, Ootbi by Object First delivers secure, simple, and powerful backup storage for Veeam customers.
Ootbi fits into the top-tier storage level. It means it is designed to store your most important and frequently used data, ensuring it is quickly and reliably accessible when you need it most.
Its high-performance capabilities support quick and efficient data recovery, minimizing downtime in case of an outage or data loss.
Read the white paper and learn why Ootbi is the best storage for Veeam.
FAQ
What Is Tiered Storage Architecture?
Tiered storage architecture organizes data into different storage tiers based on its usage and importance. This structure helps optimize performance and cost by placing frequently accessed data on high-speed media and less critical data on more economical storage solutions.
What Is Multi-tiered Storage Architecture?
Multi-tiered storage architecture expands the concept of tiered storage by incorporating multiple layers, each tailored to specific data needs and performance requirements. It typically includes several tiers, from high-performance SSDs for mission-critical data to slower, cost-effective storage for archival purposes.
What Is Automated Storage Tiering?
Automated storage tiering uses software to dynamically move data between different storage tiers based on access patterns and predefined policies. This automation ensures that frequently accessed data remains on high-speed storage while infrequently accessed data is moved to lower-cost storage.


