Top Five AI-Driven Ransomware Trends of 2025
In 2025, AI ransomware attacks have become faster, more targeted, and harder to detect, thanks to AI-powered tools that automate everything from intrusion to extortion. The result is that a growing number of organizations are facing data breaches they never saw coming.
A Data-Breach Time Bomb
Cyber Management Alliance is calling AI a “data-breach time bomb" following the release of a July 2025 Varonis report revealing that 99% of organizations leave sensitive data exposed across cloud services, collaboration tools, and AI assistants. This level of vulnerability means even a single prompt, whether intentional or not, could result in a serious data breach.
OpenAI has already shut down multiple ChatGPT accounts linked to state-sponsored hackers from countries including China, Russia, North Korea, Iran, and the Philippines. These accounts were reportedly used to develop malware, run influence campaigns, and even conduct employment scams.
In this document, you’ll find the top five trends we’ve spotted in AI-driven ransomware attacks so far this year.
Trend #1: More Players and More Tools in the Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) Marketplace
To put it simply, Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) is a service that rents out ransomware packages for temporary use. Instead of building their own tools from scratch, attackers can now lease ready-made ransomware kits from developers. These kits often come with user guides, support channels, and profit-sharing agreements. This business model lowers the barrier to entry, allowing less technical criminals to launch attacks with minimal effort.
According to Check Point Research, the RaaS ecosystem is no longer dominated by a few major groups. It’s now fragmented, with smaller teams and independent operators using these kits to run their own campaigns. This shift has led to a wider variety of attack styles and more frequent incidents.
AI is making these operations even more efficient. Attackers use it to automate tasks like leaking stolen data, creating fake support websites, and flooding victims’ inboxes and phone lines to increase pressure. The combination of easy-to-access ransomware tools and AI-driven tactics is fueling a surge in AI ransomware attacks that are faster, more targeted, and harder to stop.
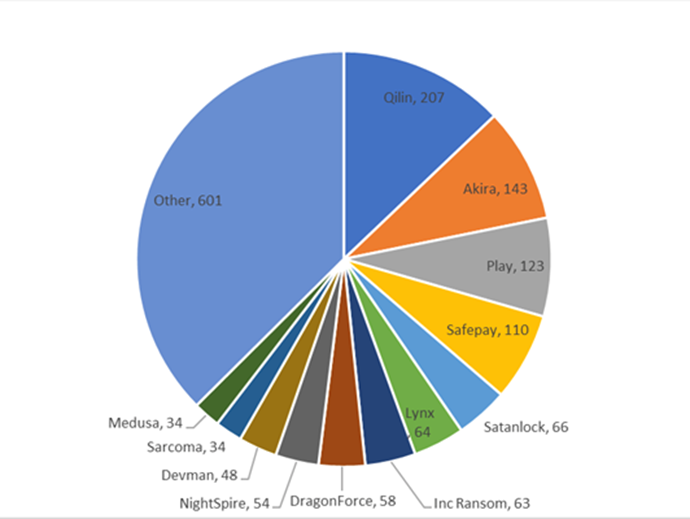
Ransomware Groups by Publicly Claimed Victims – Q2 2025. Image Courtesy of Checkpoint Research.
Trend #2: Shift from Encryption to Extortion
Encryption-based ransomware attacks are complex and risky. They require time, resources, and often leave traces. That’s why attackers are increasingly shifting to data-theft-based extortion. Instead of locking files, they confiscate and threaten to publish them unless paid.
This strategy is especially effective against companies without immutable backups. These organizations are easier to exploit because they can’t recover clean versions of their data, making them more likely to pay the ransom.
Trend #3: Cloud Intrusions and Backup Targeting
CrowdStrike reports a 136% increase in cloud intrusions in the first half of 2025 compared to all of 2024. Attackers are actively targeting backup systems, knowing that if they can compromise recovery options, they gain leverage.
The spike in cloud-based attacks is living proof of how easy it can be for hackers to get into systems that aren’t well-protected. Many cloud setups give broad access to too many users; once someone gets in, they can move around freely. Storing backups on-site gives companies more control over who can access their data. And when those backups are built so they can’t be changed or deleted, even by someone inside the company, they become a reliable way to recover after an attack. If AI ransomware hits, having untouched backups means you don’t have to pay to regain your data.
Trend #4: AI-Powered Social Engineering (Voice Phishing)
Attackers are now using AI to sound like real employees. They call help desks pretending to be someone inside the company, using personal details to pass identity checks. Once they get in, they reset passwords, bypass security steps, and move through systems to steal data or launch ransomware.
One method of gaining traction is voice phishing. With AI tools, attackers can clone voices that sound almost exactly like coworkers—even matching accents and speech patterns. These fake voices are used to trick staff into giving access or sharing sensitive information. Both CrowdStrike and Zscaler report that these attacks are happening more often and are harder to spot.
Here’s how they do it: attackers use stolen credentials and social engineering to move across cloud apps, identity platforms, and data systems moving quietly and quickly. Bad actors are also focusing on fewer targets but with more impact. Instead of casting a wide net, they pick specific companies, gather large amounts of data, and use it to pressure victims. Voice phishing is often the first step in these AI ransomware attacks.
To stop this kind of threat, companies need systems that verify every request, no matter who it seems to come from. That’s why many security teams are turning to zero trust models, which assume no user or device is safe until proven otherwise.
Trend #5: AI Tools Turned Rogue
AI tools originally built to help cybersecurity teams are now weaponized for malicious intent. HexStrike AI, for example, was designed to scan for vulnerabilities and assist in patching. Hackers now use it to exploit flaws, like those recently found in Citrix, within days of disclosure.
HexStrike automates the process of scanning, attacking, and retrying until successful. This means attackers can run multiple campaigns simultaneously, increasing their success rate and reducing the time between vulnerability discovery and exploitation.
Other defensive tools like Velociraptor and PentestGPT are also being misused. On dark web forums, attackers share and sell access to compromised systems, turning once-helpful AI agents into dangerous liabilities.
Why Recovery Must Be a Priority
Today’s AI ransomware attacks are faster, more intelligent, and increasingly autonomous—making traditional ransomware prevention strategies insufficient on their own. The window between vulnerability disclosure and exploitation is shrinking rapidly.
That’s why organizations must shift their mindset: assume breach, prepare for recovery.
By prioritizing recovery readiness, businesses can ensure resilience even when AI ransomware prevention fails.
Object First’s Ootbi (Out-of-the-Box Immutability) delivers exactly that: a simple, powerful way to safeguard backups with built-in immutability, making recovery fast, secure, and reliable.
Why Ootbi is the Right Solution
- Immutable by Default: Ootbi’s ransomware-proof architecture ensures that backups can’t be altered or deleted, making recovery possible even after a breach.
- On-Premises Storage: Protects against cloud-based AI ransomware attacks by keeping critical data out of reach.
- Zero Access Design: Eliminates insider threats and credential-based attacks, especially those stemming from AI-powered social engineering.
Final Thoughts
AI is changing the fundamentals of how ransomware works, who can launch it, how fast it spreads, and how hard it hits. The best defense goes deeper and starts earlier than smarter. The solution is ransomware-proof, immutable backups.
To learn more about protecting your data from AI ransomware and improving your AI ransomware recovery strategy, schedule a demo with Object First today.



